
THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO THE BENEFITS OF A GOOD NIGHTS KIP
By Neil O’Hanlon
The Shorter Your Sleep, The Shorter Your Life Span
Hi guys, did you have a good nights sleep? Well if not, this might be of some interest to you. I used to think that just getting by on limited amounts of shut eye was ok, especially when I was younger. I didn’t think it was affecting my day to day life or athletic performance. How wrong I was. What I know now is that sleep is the most effective thing we can do to reset our brain and body each day. Now-days I always strive for at least 7 to 8 hours of quality sleep per night and the results that come with that are second to none. No anxiety, brain fog, lethargy or fatigue, just clear headed mental alertness and physical wellbeing. I now prioritise sleep over everything else health wise.
The bridge between despair and hope is a good nights sleep
Sleep, Nutrition And Exercise In That Order

I now feel that sleep is the foundation of all health. Without getting your sleep in order, the other two pillars of health, Nutrition and Exercise just won’t work. In my opinion that’s the order to prioritise these. If I was to deprive you of food for 24 hours or deprive you of exercise for 24 hours, or both, they still would not equate to depriving yourself of sleep for 24 hours. 24 hours of no sleep is seriously problematic for all kinds of reasons, it can actually induce a pre-diabetic state as well as a whole host of other health concerns.
Sleep Is Non Negotiable
Short sleep has so many damaging effects on the cardiovascular system, on weight, raising the chances of diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as lowering your immune function, memory, and mood. If you deprive yourself of sleep or deep sleep for just one night – there’s an immediate increase in beta-amyloid proteins (present in Alzheimer’s).

Sleep should not be an optional lifestyle luxury, it is a non-negotiable biological necessity. It is your life support system.
The Single Most Effective Thing We Can Do Is
In a nutshell, the shorter your sleep, the shorter you live. Short sleep is one of the biggest predictors of all-cause mortality. Sleep really is the single most effective thing we can do each day to reset our brain and our body, as there’s not one function in the body or mind that isn’t enhanced when we get a good night of quality sleep. On the flip side these functions are demonstrably impaired when we don’t.
The shorter your sleep, the shorter your life, its as simple as that
How We Have Come To Perceive Sleep
Over time sleep has become associated with being lazy. If we are fortunate enough to get a good nights sleep 7 to 9 hours then society somehow deems that as luxurious, privileged or even slothful. In a world where there’s an increasing badge of honour to work all the hours you can and get away with as little sleep as possible is just bizarre. Most of us experience gradual chipping away of our precious sleep time and I get it. In an ever increasingly busy world there’s so much to fit in. We don’t want to shortchange on our time with family, friends or socialising, so we actually end up sacrificing sleep time instead?
Resting when tired isn’t lazy, its self care

Lack Of Sleep Affects The Ability To Lose Weight
If weight loss is your primary goal then it becomes very difficult if you don’t get enough sleep. Even if your dieting, the hormonal effect of sleep deprivation means that instead of burning fat and gaining muscle, you actually do the opposite and start gaining fat and losing muscle which is not what you want. Lack of sleep makes it easier to make wrong choices when it comes to food and will normally result in choosing high sugar, highly processed nutrient deficient types of food.
Lack of sleep means Instead of burning fat, you actually start gaining fat
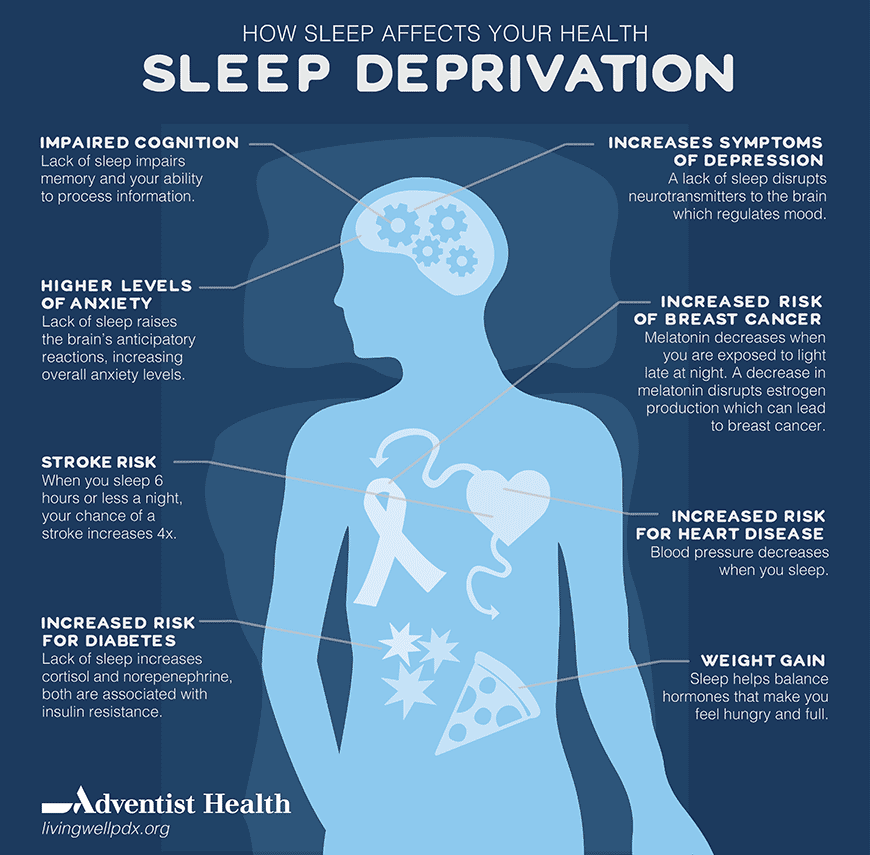
Enter Ghrelin And Leptin The 2 Hormones
The reason for this anomaly is because of two appetite-regulating hormones called Leptin and Ghrelin and no, they’re not two hobbits. Leptin is the hormone of satiety (fullness) which says to your brain and body that you are full. This is a good thing. Ghrelin is the hunger hormone that tells you to eat more. This is a bad thing. With lack of sleep, Ghrelin increases and Leptin drops away so you lose the signal of being full which in turn can lead to over consumption of calories as your body still thinks you’re hungry. Any extra calories consumed will be stored as fat.
In fact Lack of sleep as well as storing extra calories as fat can actually induce a pre-diabetic state
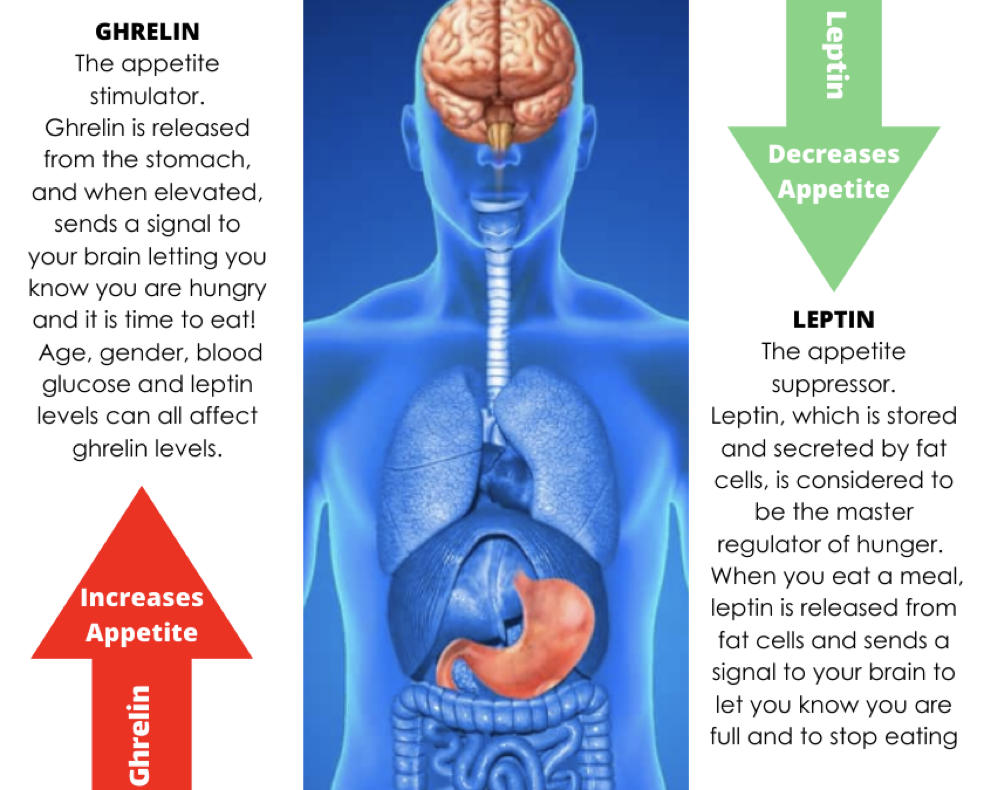
Sleep Deprivation And Exercise
With regards to lack of sleep and trying to exercise. If you obtain anything less than eight hours of sleep a night, and especially less than six hours a night, then the following happens. You’re time to physical exhaustion drops by 10 to 30 percent, and aerobic output is significantly reduced. Similar results show decreases in peak and sustained muscle strength, reduction in cardiovascular, metabolic, and respiratory capabilities that will hamper an under slept body significantly.
This would show up in faster rates of lactic acid buildup, reductions in blood oxygen saturation, and increases in blood carbon dioxide, due in part to a reduction in the amount of air that the lungs can expire. Even the ability for the body to cool itself down during physical exertion through sweating which is a critical part of peak performance, even this is impaired by sleep loss. Sleep is also vitally important after physical exertion, especially hard efforts. Post-performance sleep accelerates physical recovery from common inflammation, stimulates muscle repair, and helps restock cellular energy in the form of glucose and glycogen which is the body’s first fuel source.
Sleep is our bodies emotional first aid kit
Sleep And General Health
A lack off, or not enough sleep has devastating effects on the brain, linking it to numerous neurological and psychiatric conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, suicide, stroke, and chronic pain. Every physiological system of the body is affected by sleep loss which further contributes to countless other disorders and disease like cancer, diabetes, heart attacks, infertility, weight gain, obesity, and immune deficiency. No part of the human body is spared the crippling, toxic harm of sleep loss.One brain function that buckles under even the smallest dose of sleep deprivation is concentration. The deadly consequences of a lack of concentration is always most obviously and fatally in the form of drowsy driving.
Every hour, someone dies in a traffic accident due to a fatigue-related error. Not only this, but participants who are sleep deprived consistently underestimate the degree to which their performance is reduced.
We as humans need at least seven hours of sleep each night to at least maintain cognitive performance.
After ten days of just seven hours of sleep, the brain is as dysfunctional as it would be after going without sleep for twenty-four hours.
Sleep Quality & Cardiovascular Disease
This may shock you, it certainly did for me when I researched it. When we put the clocks forward in Spring, because there is more daylight hours, there is actually a 24% increase of heart attacks in spring and a 21% reduction in heart attacks in Autumn when the clocks go back. This basically tells us that people are getting considerably less sleep in the Spring and Summer due to the extended daylight hours. If you’re someone who consistently get less than 6 hours of sleep a night then studies have shown you may have a 200% increased risk of cardiovascular disease or heart attack. Shocking!
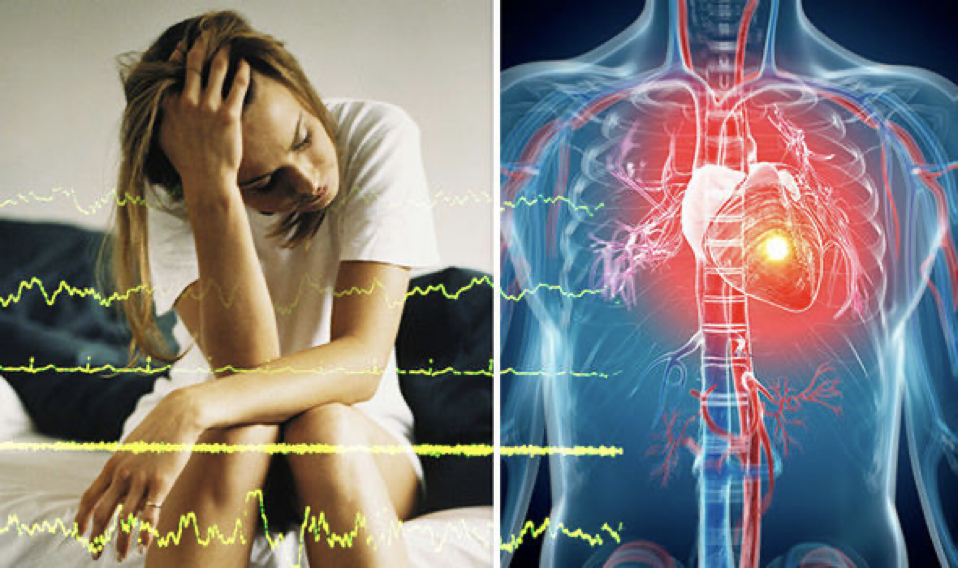
Less Than 6 Hours Sleep A Night Can Be Fatal
As well as this people who have no pre-existing record of heart disease but are also sleeping less than 6 hours per night have a 200 to 300% increase in calcification of the coronary arteries – (blocking off the arteries). That’s just by getting 1 or 2 hours less sleep a night than someone else.The reason for the above facts are that short sleep and fragmented sleep have a high likelihood of hardening blood vessels which can be the pathway to cardiovascular disease and heart attack.
However during deep sleep, our heart rate decelerates and our respiratory rate is low. If you are chronically high in heart rate and respiratory rate, blood pressure will be affected in your wakeful hours. During deep sleep we shift from sympathetic nervous system which is the ‘Fight or Flight’ system to the parasympathetic nervous system which is the ‘Rest and Recovery’ system and our bodies start to heal.
Sleep is just as critical as other diet and lifestyle factors for cardiovascular health
Sleep And Alzheimers
In general, sleep is critical for memory. A lack of sleep is fast becoming recognised as a key lifestyle factor determining whether or not you will develop Alzheimer’s disease in later life. People who sleep less than 6 hours per night develop far more chance of getting Alzheimer’s disease. This may include people with Insomnia but even healthy sleepers. If you deprive a healthy adult of sleep or deep sleep for just one night, there’s an immediate increase in beta-amyloid proteins, this is the protein that’s present in the brain that causes Alzheimer’s.
If you want to avoid Alzheimer’s disease, sleep 8 hours a night
However on a positive note the brain has a cleansing system called the Glymphatic system which kicks in during deep sleep. It washes away the beta-amyloid protein (Alzheimers Protein) which in turn helps fight against Alzheimer’s disease. Sleep could well be the missing piece in the puzzle of premature ageing and Alzheimer’s disease.
The elastic band of sleep deprivation will stretch only so far before it snaps. If you fight biology, normally you lose

Tired and Forgetful?
In other words, if you don’t sleep the very first night after learning something new, you lose the chance to bank those memories, even if you get lots of catch-up sleep thereafter. Research has showed a loss of memory structure in the brain’s of airline pilots whose schedules mean they are sleep deprived due to time changes and flight times.
Sleep Loss and the Immune System
There’s an intimate association between sleep health and immune health. Sleep deprivation vastly increases your likelihood of infection, and reduces your response to the flu vaccine. In fact Individuals who sleep less than 7 hours per night are almost 3 times as likely to contract rhinovirus (common cold). Women sleeping 5 hours or less per night are more than 60% more likely to develop pneumonia.
On top of that, If you don’t get enough sleep in the week before a flu shot, you will not have the same level of antibody response.
Lack of sleep in men causes testosterone drops equivalent to ten years of ageing. Lack of sleep in women is damaging to menstrual cycles and fertility health
Delusional Thoughts
Some people are so disillusioned to how many hours sleep they think they can actually get away with. Most people cannot survive on five hours of sleep or less with no repercussions. We just convince ourselves to think we’re invincible or that we don’t need much sleep. This kind of ‘Sleep when you’re dead’ mentality is dangerous and may even bite you on the arse in later life. Short sleep or insufficient sleep clouds judgment of our experience and necessity of sleep hours. In a culture full of quick wins and hacks its detrimental to think we can hack our sleep. The effects of sleep deprivation vary but common outliers are psychosis, personality changes, changes in appetite, memory loss, and emotional instability. In a sentence, the deficient version of yourself becomes the new normal you.
Anxiety is the principal cause of Insomnia – for better sleep, get physical activity and deal with anxiety without pills – try meditation or mindfulness
How to Choose the Best Sleeping Position
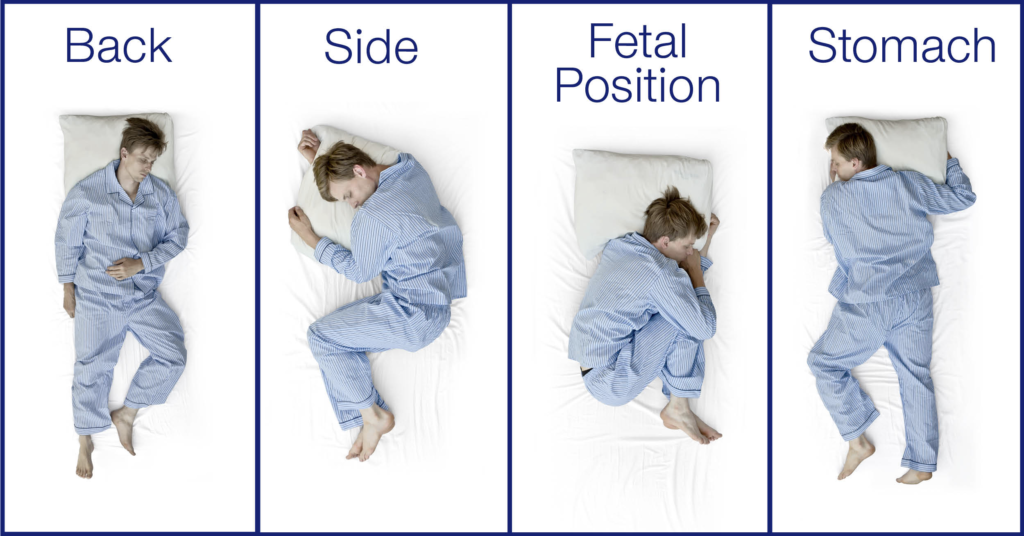

Good sleep is crucial for our physical and mental well-being. One key nighttime variable for a restful sleep is your preferred sleep position. While most people naturally prefer a particular sleep posture, each position has its unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these pros and cons can be the difference between a good night’s snooze and waking up on the wrong side of the bed. There are four common sleep positions, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
On your side: A side-sleeper is a person who prefers lying on their left or right side in bed, either with their legs straight or slightly curled. Side-sleeping can help reduce heartburn and indigestion. However lying on your side for prolonged periods can result in alignment issues, making you more prone to lower back, neck, hip, and shoulder pain the next day.
On your back: A back-sleeper is a person who prefers lying flat on their back in bed. Back-sleeping offers good spinal support as long as you have a decent mattress. However sleeping on your back can aggravate breathing-related sleep conditions, like snoring or obstructive sleep apnea.
On your stomach: A stomach sleeper is a person who prefers lying on their stomach, either flat or at a slight angle to one side in bed. Stomach-sleeping can reduce snoring, however stomach-sleeping comes with a high risk of neck, shoulder, and low back pain due to the spine’s unnatural position.
In the foetal position: The foetal position is when a person sleeps on their side with their legs curled into their chest. The foetal position can help relax the spine and feel more natural. Although the foetal position may be the most comfortable, if you sleep in an especially tight curl, you can put a lot of strain on your joints and back, as well as obstruct your airway and prevent your body from oxygenating properly.
Room temperature, Bedtime regularity, caffeine and alcohol intake, exercise, and physical activity all help sleep
Are Naps Any Good

Polyphasic sleep which is multiple periods of sleep throughout 24 hours doesn’t work. There’s no evidence that anything in our biology suggests we’re designed to have multiple bouts of sleep.
However, there is an argument to be made for biphasic sleep, which means we sleep for 6-7 hours at night then siesta a few hours during the day. The thing is naps are a double-edged sword. If you struggle with sleep and insomnia then its best not to nap during the day in the false attempt to build up sleepiness and hopefully sleep at night as this just won’t work. All you end up doing is releasing healthy sleep pressure that’s built up for later and wasting it on an afternoon nap. What I would say though, If you don’t have sleep problems or insomnia then naps before 2pm are ok. Many people have that afternoon slump of daily sleepiness from 2-4pm. It could be possible that our natural sleep pattern is designed to nap at that period. For every individual it’s going to be a case of trial and error.
When Greece experimented with eliminating siesta, cardiovascular health decreased so much so that there was between a 30-60% increase in the likelihood of heart attack
Caffeine And Sleep
Caffeine can damage sleep due to the timing of caffeine in the body. The problem is caffeine has an 8-hour half-life which means if you had a cup of coffee at noon, then half the caffeine from the coffee is still in your system at 8pm. Even worse, caffeine has a quarter life of 12 hours so this would be the same as drinking a quarter of a cup of Costa at midnight just before bed. You just wouldn’t do it. It also decreases the quality and quantity of non-REM deep sleep. I would try to drink your coffee before 11am in the morning to at least try and get a good nights kip.

Alcohol And Sleep
Remember Alcohol is not a sleep aid but a sedative. However sedation is not to be confused with sleep. Alcohol fragments your sleep so you keep waking throughout the night which means you lose out on vital REM restorative sleep.
Alcohol-infused sleep is therefore not continuous and, as a result, not healing. Unfortunately, most of these nighttime awakenings go unnoticed by the sleeper since they don’t remember them.
Alcohol is one of the most powerful suppressors of REM sleep that we know of. Many people enjoy a glass of wine with dinner, or a beer after work to unwind. But it takes your liver and kidneys many hours to degrade and excrete that alcohol. Nightly alcohol will disrupt your sleep. If you really struggle to sleep then the annoying advice of abstinence is the best and most honest I can offer. However, I would be a hypocrite to suggest this, as I myself love to imbibe in a cold one after work.
Even a glass of wine with dinner has an impact on sleep

Blue Light And Sleep
Compared to reading a good old fashioned printed book, reading on an iPad or phone suppresses melatonin (the hormone that makes us sleepy) release by over 50 percent at night. The fact is that using an iPad or Kindle to read can delay the rise of melatonin by up to three hours. This means you’re still wired 3 hours later after getting into bed as opposed to reading a printed book. When it comes to trying to calm down on the artificial lighting, a good start is to create lowered, dim light in the rooms where you spend your evening hours. Avoid powerful overhead lights. Mood lighting and candles are perfect.
As I mentioned earlier, I have started wearing some blue light blocking glasses indoors in the evening to help filter out the most harmful blue light that suppresses melatonin and ultimately stops us getting sleepy. As well as this its essential to maintain complete darkness throughout the night. The easiest fix for this is blackout curtains.

Hot Bath And A Cool Room For Great Sleep
It’s important to keep the bedroom cool in order to get a good nights sleep. A bedroom temperature of around 65 degrees Fahrenheit (18.3°C) is ideal for most of us. A luxury for many is to have a hot bath in the evening and soak the body before bedtime. We feel it helps us fall asleep more quickly, which it can, but for the opposite reason most people imagine. You do not fall asleep faster because you are toasty and warm to the core. Instead, the hot bath invites blood to the surface of your skin, giving you that flushed appearance. When you get out of the bath, those dilated blood vessels on the surface quickly help radiate out inner heat, and your core body temperature goes down. As a result of this you fall asleep more quickly because your core is colder.
Hot baths prior to bed can also induce 10 to 15 percent more deep NREM sleep in healthy adults.

Sleep Cycles In Humans
There are two main types of sleep. Non-rapid eye movement sleep (non-REM) and rapid eye movement (REM).
Non-REM sleep has four cycles:
Stages 1 and 2 are light stages of sleep
Stages 3 and 4 are deep stages of sleep
REM sleep however is the stage in which we dream and effectively repair ourselves with overnight therapy. When we go into REM dream sleep, the brain paralyses the body so you won’t be able to act out your dreams. Obviously this is a good thing. So if you’ve ever had that dream where you need to run or shout and nothing happens, this is precisely the reason why. It’s totally normal but freaky at the same time. When we get deep sleep, it allows us to save memories in the brain. The first half of the night is dominated by non-REM deep sleep, and the second half of our sleep is dominated by REM sleep. All stages of sleep are critical but there is some research suggesting REM sleep may be slightly more important for helping us live longer. Because we sleep in 90-minute cycles, it makes a difference if we decide to shift our sleeping pattern to either sleep later or wake up earlier.
REM sleep is what stands between rationality and insanity.
Natural Ways To Sleep And Pills
Darkness triggers the natural release of melatonin. In order to get this naturally, try dimming the lights in the house in the evening and avoiding all kinds of blue light that comes from mobile phones, laptops, tv’s and tablets. In the first half of the day, try to get at least 40 minutes of direct sunlight each morning to feel more alert and regulate the natural circadian rhythm.
Circadian rhythms are 24-hour cycles that are part of the body’s internal clock, running in the background to carry out essential functions and processes.
Prescription sleeping pills have a purpose in acute scenarios such as a grievance or trauma. However they are only recommended for short term use and in combination with therapy in most cases.
The problem is the rebound effects of sleeping pills. Once you stop taking them then your sleep quality is normally worse.
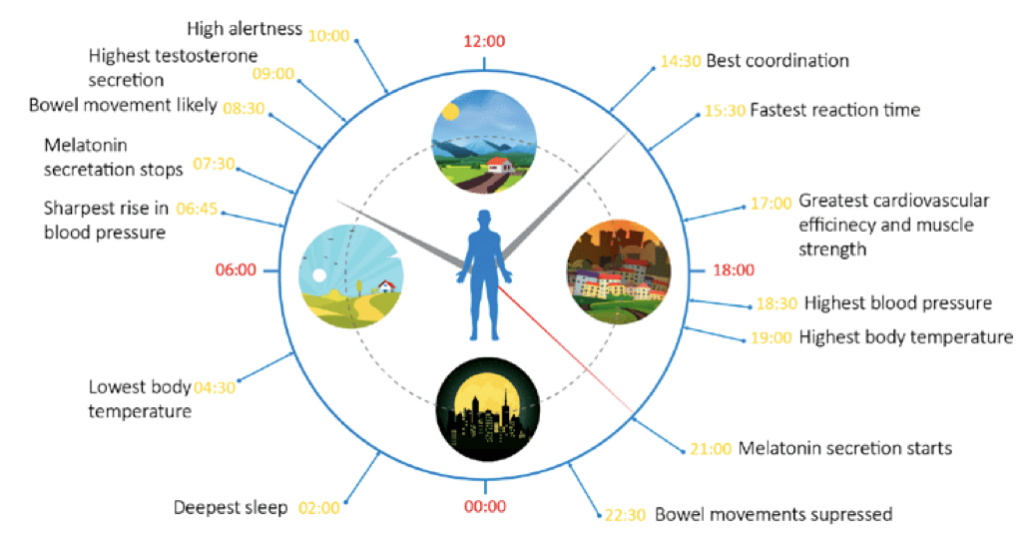
How To Sleep Better Simplified
For better sleep, the main things you can do are control the temperature in your bedroom, try to have some kind of routine where you go to bed and wake up at the same time everyday, even on weekends, and even if you’ve had a bad night of sleep. Keeping it regular really does increase quality and quantity of sleep.Try to limit your caffeine and alcohol intake, get enough exercise preferably in the mornings, and have a wind down routine for the last hour before bed. This could be reading a book, having a hot bath (which is a proven method) or meditation, just try to stay away from electronic devices like your phone and television that stimulates your brain with copious amounts of blue light. I myself have a pair of blue light blocking glasses that I wear one hour before bed and this definitely helps to start unwinding. We are on the go so much these days that we don’t reflect on our day until our head hits the pillow and this is completely the worst time of day to reflect. At this point, good sleep will be hard to come by.
We start over thinking, worrying and catastrophising everything in our heads.
Don’t Count Sheep
To help drift off naturally, try to visualise a walk you have taken, a hike or just anything you enjoy doing. Don’t count sheep it stimulates the brain too much. Meditation is something else to try if you have problems sleeping. This can decrease the severity of insomnia more effectively than medication. Keep the room cool as our body needs to drop in core temperature to fall asleep and more importantly stay asleep. It’s much more comfortable and easier to sleep in a cold room versus a warm room.
This is exactly why it can help to keep our hands and feet out of covers. Hands and feet are radiators of heat because they are highly vascular. By keeping our extremities on the outside we are evacuating the heat from our bodies to cool down. Another key tip if you’re struggling to get to sleep is to avoid lying in bed for too long. Lying in bed for prolonged periods, hoping you’ll finally nod off, isn’t an effective sleep strategy, however it can make you anxious and frustrated. Your brain will associate bed with being awake if you do anything in it besides sleeping or sex. If you cannot fall asleep after about 25 to 30 minutes of lying in bed, get up and do a relaxing activity, read a book, try a breathing practice or just sit in a dim room until you start feeling sleepy. Only at that point, go back to bed!
Going to bed and waking up at the same time of day no matter what, is perhaps the single most effective way of helping improve your sleep, even though it involves the use of an alarm clock.
Tips To Help You Get A Good Nights Sleep
Find A Routine
Your body’s internal clock follows a specific sleep-wake cycle. Going to bed late one night and early the next throws your circadian rhythm off balance. Attempting to catch-up on missed sleep (sleep deficit) over the weekend may not always be effective and can result in physical and mental fatigue. Thus, adhering to a daily sleep schedule can be highly beneficial for your overall health and well-being.
Cut The Late-Night Cardio.
If you’re feeling run-down in the morning, your late-night workout on the treadmill may be to blame. For some, a midnight workout or intensive yoga session too close to bedtime can make it harder for the brain to wind down. Aim to finish heavy exercise two to three hours before hitting the sack.

Reduce Caffeine And Nicotine Consumption
Caffeine temporarily blocks the signal from adenosine, a crucial sleep chemical in your brain, which nonetheless continues to accumulate. This pent-up adenosine eventually breaks through, causing a dramatic crash, often at inopportune times. Nicotine, another stimulant, can lead to very light sleep and its the deep restorative sleep we are after
Cut Down On The Alcohol
Alcohol before bed may help you relax, but too much of it can contribute to a lack of sleep. Alcohol robs you of deep REM sleep, the deep slumber your brain requires for optimal restoration. Heavy alcohol consumption can also impair your breathing at night. Also its not good for staying asleep. You tend to wake up multiple times, even if you don’t remember doing so.

Eat Light At Night Not Late
When it comes to late-night eating, small snacks are preferable to heavy meals, which can cause indigestion that interferes with your sleep. Avoid drinking fluids a couple of hours before bedtime to prevent frequent bathroom trips in the middle of the night, interrupting sleep, which can lead to sleep fragmentation.
Leave Time To Unwind
Create a relaxing routine before bed, like reading, listening to music, or doing some light stretching. You may wish to keep a worry journal, which can help you process difficult emotions before bed. Putting it down on paper can seriously lessen the initial worry and put it in perspective. Things aren’t that bad.

Baths Are Best
It sounds paradoxical, but taking a hot bath before bed can drop your body temperature once you’re in bed, in addition to making you feel sleepier and more relaxed. Think of the ideal bedroom as a prehistoric cave somewhere in the Great North, cool, dark, and blue light-free. Charge your phone in another room, get rid of electronics that cause noise, and ditch the alarm clock, which can make you hyper-aware of every passing minute.
Get Some Sun
Exposing yourself to natural sunlight for at least 30 minutes a day can help regulate your sleep patterns. Aim to catch those rays in the morning, which can make you more alert as you start your day. Also, turn the lights down before bedtime to avoid disrupting melatonin production. Remember melatonin is the sleep hormone we need to drift off to Telly Tubby Land.

Talk To Your Doctor About Your Medication
Some heart and lung medications, and over-the-counter cold and allergy drugs, can disrupt sleep patterns. If you have trouble sleeping, ask your doctor or pharmacist if medication may be the culprit, and whether you can take them earlier in the day.
The brain is 30% more active during sleep than when awake
Sleep And Full Moon
Don’t worry I’m not talking about turning into a werewolf, but there is conflicting evidence that people sleep less when there’s a full moon. The reason being that sleep duration decreases when there’s a full moon due to the brightness of the moon which can decrease melatonin in the brain.
If we think about the origin of the word “lunatic”, it’s related to lunar patterns and the shifts in how people act

Twelve Quick Tips For Healthy Sleep
- Stick to a sleep schedule
- Exercise is great, but not too late in the day. Try to exercise at least thirty minutes on most days but not later than two to three hours before your bedtime.
- Avoid caffeine and nicotine before bed..
- Avoid alcoholic drinks before bed.
- Avoid large meals and beverages late at night.
- If possible, avoid medicines that delay or disrupt your sleep.
- Don’t take naps after 3 p.m.
- Relax before bed. Don’t over schedule your day so that no time is left for unwinding. A relaxing activity, such as reading or listening to music, should be part of your bedtime ritual.
- Take a hot bath before bed.
- Dark bedroom, cool bedroom, gadget-free bedroom.
- Have the right sunlight exposure. Daylight is key to regulating daily sleep patterns. Try to get outside in natural sunlight for at least thirty minutes each day. If possible, wake up with the sun or use very bright lights in the morning.
- Don’t lie in bed awake.
The Takeaway

Sleep had always been something I’ve just accepted as part of my daily routine. I never really cared about how much sleep I needed or the quality of the sleep I got. It was never a major issue or so I thought when it came to exercise and performance. However knowing what I know now, and the information I’ve given you in this article, sleep is the most understated and underrated pillar of good health in all areas of life. A good nights sleep solves loads of problems and even if you can’t solve them, it at least makes them manageable. My fitness and performance has benefited from prioritising sleep over the last few years and the ability to function daily without brain fog has also been a god send. Like I said earlier, if we can get our sleep in order the rest of the puzzle of good health will follow effortlessly.
